Understanding the difference between Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN), and Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS) is crucial for anyone involved in the management of laboratory data. Each system serves a unique role in the lifecycle of laboratory data management.
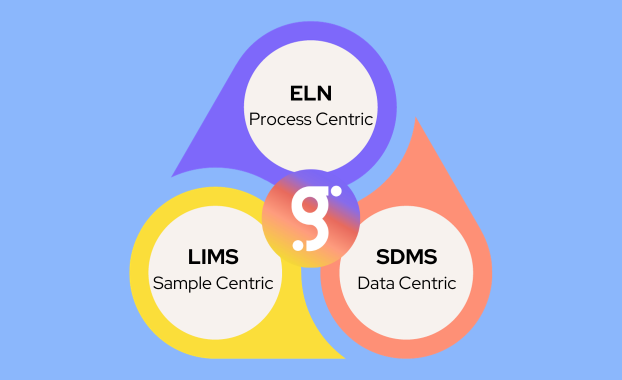
What is a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS)?
Purpose:
LIMS is designed to track and manage samples and associated data in laboratories. They are often used in clinical, environmental, and quality control laboratories.
Key Features:
- Sample tracking: LIMS systems can track a sample from receipt through processing and testing.
- Workflow Management: LIMS can automate workflows and standard operating procedures.
- Reporting and Compliance: They help in generating reports and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Quality Control: LIMS often include features for managing quality control processes.
What is an Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN)?
Purpose:
ELNs are digital versions of traditional paper lab notebooks. They are used for documenting experiments, procedures, and outcomes.
Key Features:
- Digital Recording: ELNs allow for the electronic recording of experimental procedures, observations, and results.
- Collaboration: They facilitate sharing and collaboration among researchers.
- Data Integration: ELNs can often integrate with other software systems, including LIMS and SDMS.
- Intellectual Property Protection: ELNs provide a secure way to document research for patent and intellectual property purposes.
What is a Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS)?
Purpose:
SDMS is focused on the storage, management, and analysis of large volumes of scientific data.
Key Features:
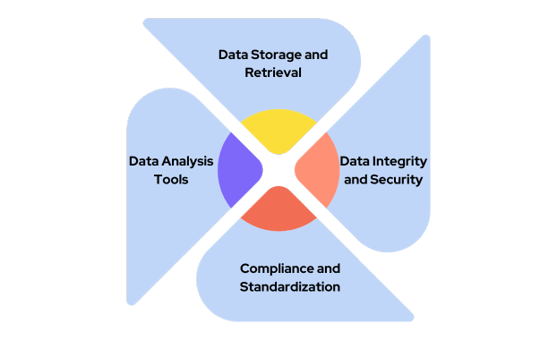
- Data Storage and Retrieval: SDMS provides robust systems for storing and retrieving large datasets.
- Data Integrity and Security: They ensure that data remains unaltered and secure.
- Compliance and Standardization: SDMS aids in maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
- Data Analysis Tools: These systems often include or integrate with tools for data analysis and visualization.
How to Integrate ELN, LIMS, and SDMS?
Focus: LIMS are sample-centric, ELNs are process-centric, and SDMS are data-centric.
Functionality: LIMS manages the logistics of laboratory operations, ELNs document the experimental process, and SDMS handles the data resulting from those experiments.
Integrating Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN), and Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS) offers a range of advantages that streamline laboratory operations, enhance data integrity, and improve overall research efficiency. Here are some of the key benefits of such an integrated system:
Streamlined Workflow and Efficiency: An integrated system eliminates the need to manually transfer data between different platforms, reducing the risk of errors and saving time. It allows for a seamless workflow from sample tracking (LIMS) to experiment documentation (ELN) to data analysis and storage (SDMS).
Enhanced Data Integrity and Security: Data integrity is crucial in laboratory environments. An integrated system ensures consistent data handling and security protocols across all stages of data management. This uniformity reduces the risk of data corruption or loss during transfers between different systems.
Improved Data Accessibility and Sharing: Integration facilitates easier access and sharing of data among team members. Researchers can quickly access sample information, experimental procedures, and analysis results from a single platform, fostering collaboration and accelerating the research process.
Comprehensive Compliance and Auditing: Compliance with regulatory standards is simplified with an integrated system. It provides a comprehensive audit trail across all aspects of laboratory operations, from sample management to experiment documentation and data analysis, ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Advanced Data Analysis and Reporting: With all data centralized, the integrated system can leverage more powerful analysis tools and generate comprehensive reports that combine information from all stages of the research process. This leads to more insightful conclusions and informed decision-making.
Cost and Resource Efficiency: An integrated system can be more cost-effective than maintaining separate systems for LIMS, ELN, and SDMS. It reduces the need for multiple software licenses, and training for different systems, and minimizes IT infrastructure complexity.
Customization and Scalability: Integrated systems often offer greater customization and scalability options. Laboratories can tailor the system to their specific needs and easily scale up as those needs grow.
Real-Time Monitoring and Decision Making: The integration enables real-time monitoring of laboratory processes and data. This immediate access to information allows for quicker decision-making and adjustments in research protocols.
Improved Quality Control: With all data and processes logged in a unified system, monitoring and maintaining quality standards becomes more efficient. It allows for immediate identification and rectification of any issues that arise during laboratory operations.
Facilitates Research Innovation: By reducing administrative burdens and streamlining data management, an integrated system frees researchers to focus more on innovation and less on the logistical aspects of data handling.
LIMS, ELN, and SDMS each play a distinct but complementary role in the management of laboratory information. The integration of LIMS, ELN, and SDMS into a single, cohesive system offers a powerful tool for laboratories. It enhances efficiency, data integrity, and compliance, while also fostering a more collaborative and innovative research environment.